I am currently a Faculty Chair of Jay Chaudhry Software Innovation Centre at the Indian Institute of Technology (BHU) Varanasi and also an associated faculty member in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering.
I am also an Honorary Fellow at the University of Surrey, UK where I collaborate with Prof. Yu Xiong on decentralised AI.
My PhD research deals with the quantum-inspired information retrieval framework with a focus on user-oriented IR, where I investigated how users' information needs can be ascertained during their search behaviour using Information Foraging Theory. My research spans across formal information retrieval (IR) models, in particular, the mathematical formalism(s) behind Quantum Theory; Quantum Probability, Hilbert space and their usage in the study of contextual information retrieval. Besides information retrieval, I am also interested in the synergy between machine learning/deep learning and quantum probabilistic frameworks, and their applications in finance and healthcare sector.
I began my bachelor studies in Computer Science at the Chhatrapati Shahu Ji Maharaj University (formerly Kanpur University) in India, culminating in a PhD in Quantum Information Retrieval under the supervision of Dr. Haiming Liu and Dr. Ingo Frommholz from University of Bedfordshire, where I was a Marie Skłodowska-Curie fellow within the QUARTZ ITN consortium. Following my PhD, I joined the department of Statistics as a Research Engineer within the School of Mathematics at University of Leeds, where I worked with Dr. Leonid Bogachev on rapid prototyping of statistical machine learning approaches focussed on Financial AI projects which spin-out as 4-XTRA Technologies Ltd. In April 2022, I moved to the University College London (UCL) as a Postdoctoral Research Fellow, where I worked with Prof. Alexey Zaikin and Dr. Oleg Blyuss on developing statistical machine learning and deep temporal vision models for risk stratification of Prostate cancer progression. From April 2023 onwards, I was a Postdoctoral Research Fellow at the University of Surrey, working on applied research at the intersection of Generative AI, Web 3.0, and Blockchain.
Before graduate school, I was also a part of Google Summer of Code program and the Linux Foundation as an intern with Kubernetes, CNCF and Openstack team at the Open Mainframe Project.

What's new?
Publications
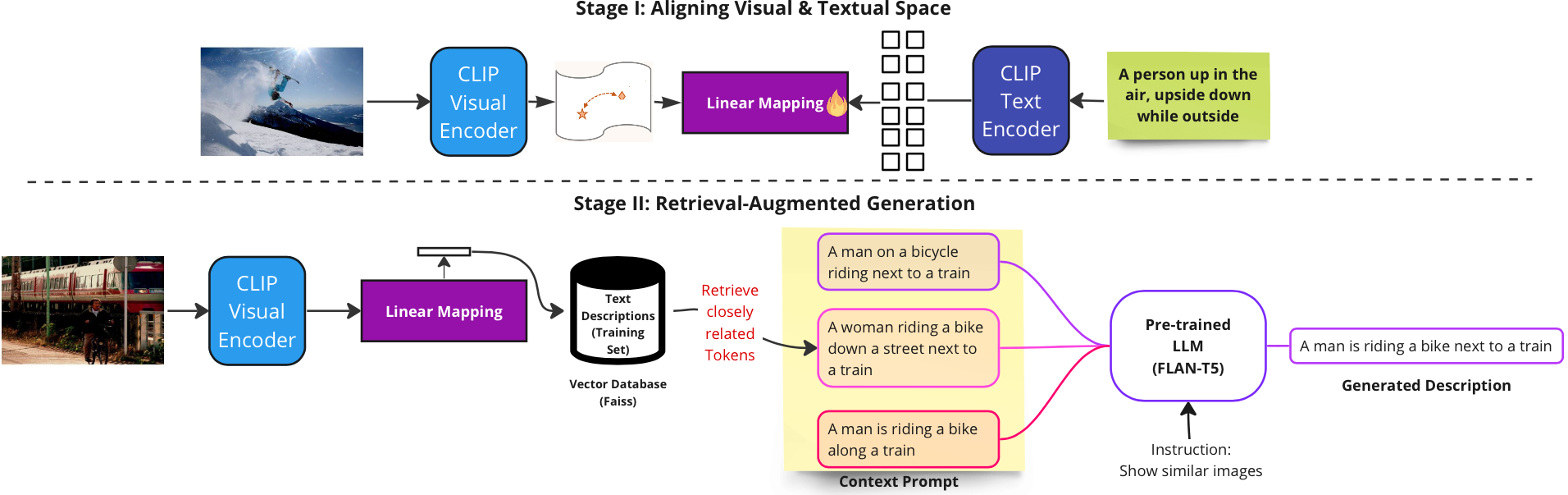
Multimodal RAG Enhanced Visual Description
Amit Kumar Jaiswal, Haiming Liu, Ingo FrommholzIn Proceedings of the 34th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM ’25),
Textual descriptions for multimodal inputs entail recurrent refinement of queries to produce relevant output images. Despite efforts to address challenges such as scaling model size and data volume, the cost associated with pre-training and fine-tuning remains substantial. However, pre-trained large multimodal models (LMMs) encounter a modality gap, characterised by a misalignment between textual and visual representations within a common embedding space. Although fine-tuning can potentially mitigate this gap, it is typically expensive and impractical due to the requirement for extensive domain-driven data. To overcome this challenge, we propose a lightweight training-free approach utilising Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to extend across the modality using a linear mapping, which can be computed efficiently... ...
[ Paper ] [ Code ] [ Poster ] [BIBTEX ]
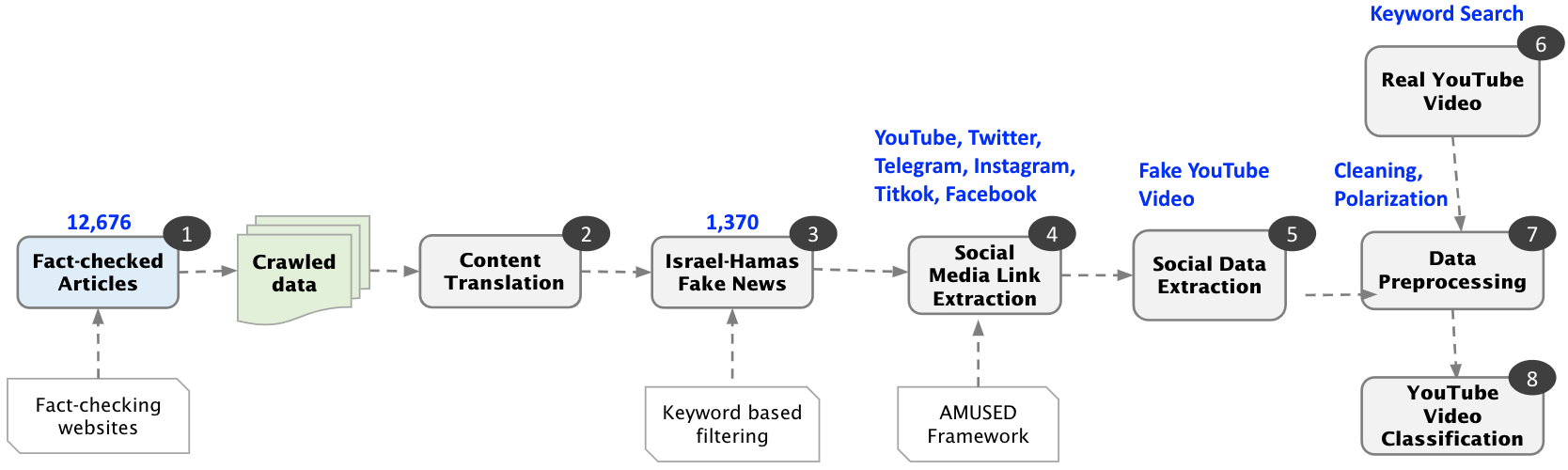
FakeClaim: A Multiple Platform-Driven Dataset for Identification of Fake News on 2023 Israel-Hamas War
Gautam Kishore Shahi, Amit Kumar Jaiswal, Thomas MandlIn Proceedings of the 46th European Conference on Information Retrieval (ECIR) (IR4Good Track 2024)
We contribute the first publicly available dataset of factual claims from different platforms and fake YouTube videos on the 2023 Israel-Hamas war for automatic fake YouTube video classification. The FakeClaim data is collected from 60 fact-checking organizations in 30 languages and enriched with metadata from the fact-checking organizations curated by trained journalists specialized in fact-checking. Further, we classify fake videos within the subset of YouTube videos using textual information and user comments. ...
[ Paper ] [ Code ] [ Poster ] [BIBTEX ]
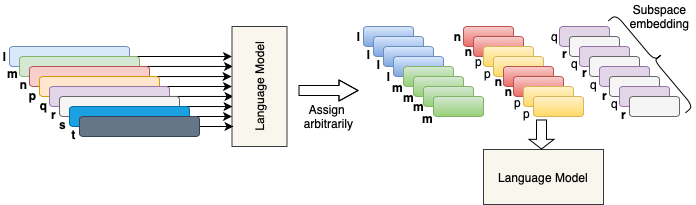
Lightweight Adaptation of Neural Language Models via Subspace Embedding
Amit Kumar Jaiswal, Haiming LiuIn Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM 2023)
Traditional neural word embeddings are usually dependent on a richer diversity of vocabulary. However, the language models recline to cover major vocabularies via the word embedding parameters, in particular, for multilingual language models that generally cover a significant part of their overall learning parameters. In this work, we present a new compact embedding structure to reduce the memory footprint of the pre-trained language models with a sacrifice of up to 4\% absolute accuracy. The embeddings vectors reconstruction follows a set of subspace embeddings and an assignment procedure via the contextual relationship among tokens from pre-trained language models. ...
[ Paper ] [ Code ] [ Poster ] [BIBTEX ]
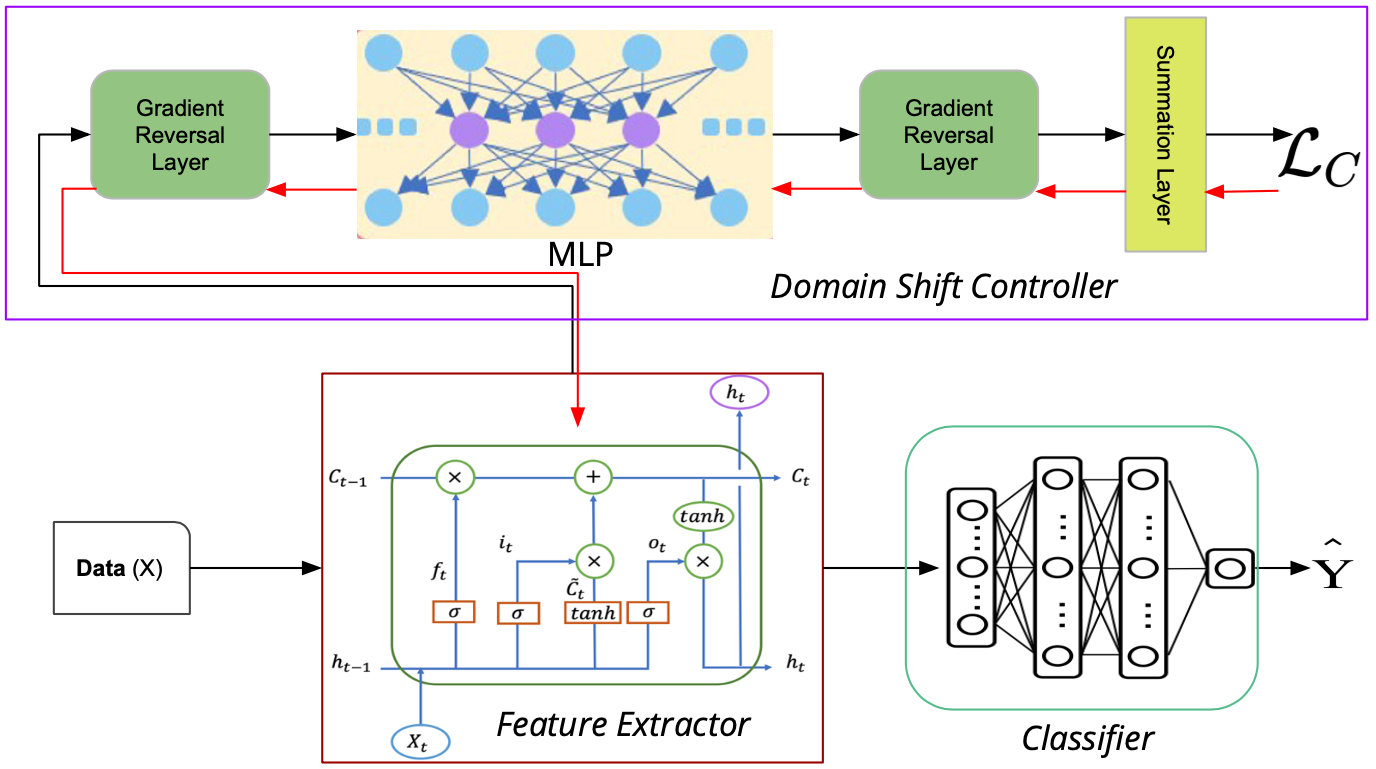
Towards Subject Agnostic Affective Emotion Recognition
Amit Kumar Jaiswal, Haiming Liu, Prayag TiwariIn Proceedings of the 2nd MUWS Workshop at the 32nd ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM 2023)
This paper focuses on affective emotion recognition, aiming to perform in the subject-agnostic paradigm based on EEG signals. However, EEG signals manifest subject instability in subject-agnostic affective Brain-computer interfaces (aBCIs), which led to the problem of distributional shift. Furthermore, this problem is alleviated by approaches such as domain generalisation and domain adaptation. Typically, methods based on domain adaptation confer comparatively better results than the domain generalisation methods but demand more computational resources given new subjects. We propose a novel framework, meta-learning based augmented domain adaptation for subject-agnostic aBCIs. ...
[ Paper ] [ Slides ] [BIBTEX ]
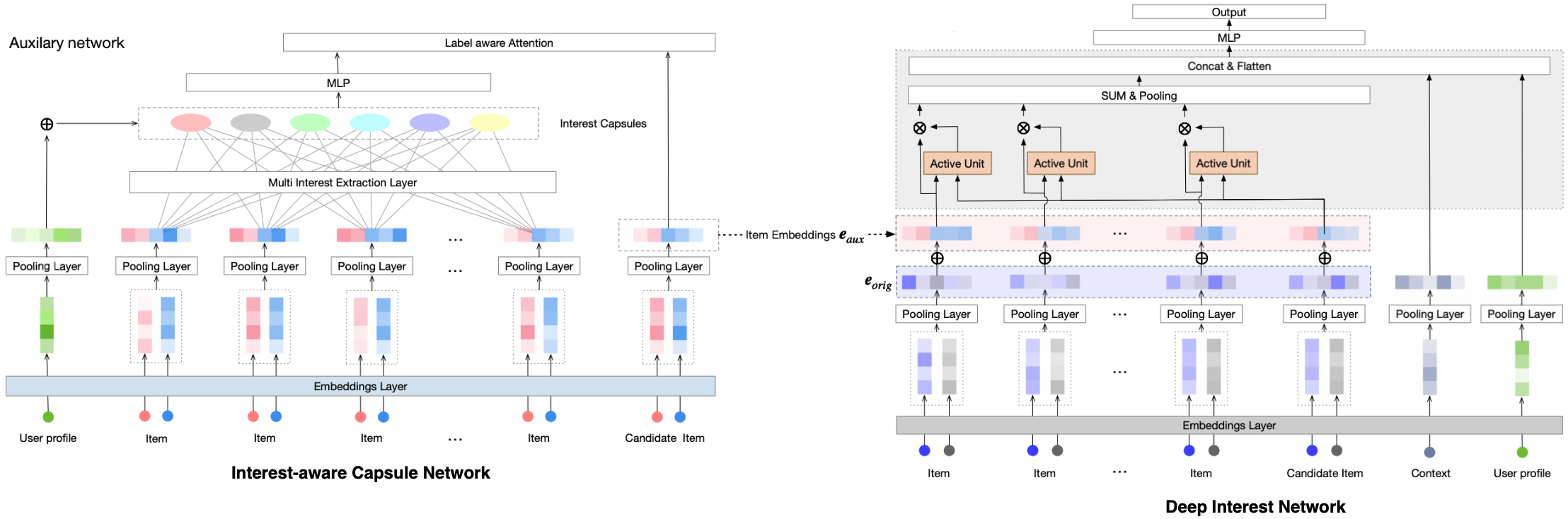
A Model-Agnostic Framework for Recommendation via Interest-aware Item Embeddings
Amit Kumar Jaiswal, Yu XiongIn Proceedings of the 17th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems (RecSys 2023) Late-Breaking Results
Item representation holds significant importance in recommendation systems, which encompasses domains such as news, retail, and videos. Retrieval and ranking models utilise item representation to capture the user-item relationship based on user behaviours. While existing representation learning methods primarily focus on optimising item-based mechanisms, such as attention and sequential modelling. However, these methods lack a modelling mechanism to directly reflect user interests within the learned item representations. Consequently, these methods may be less effective in capturing user interests indirectly. To address this challenge, we propose a novel Interest-aware Capsule network (IaCN) recommendation model, a model-agnostic framework that directly learns interest-oriented item representations... ...
[ Paper ] [ Poster ] [BIBTEX ]
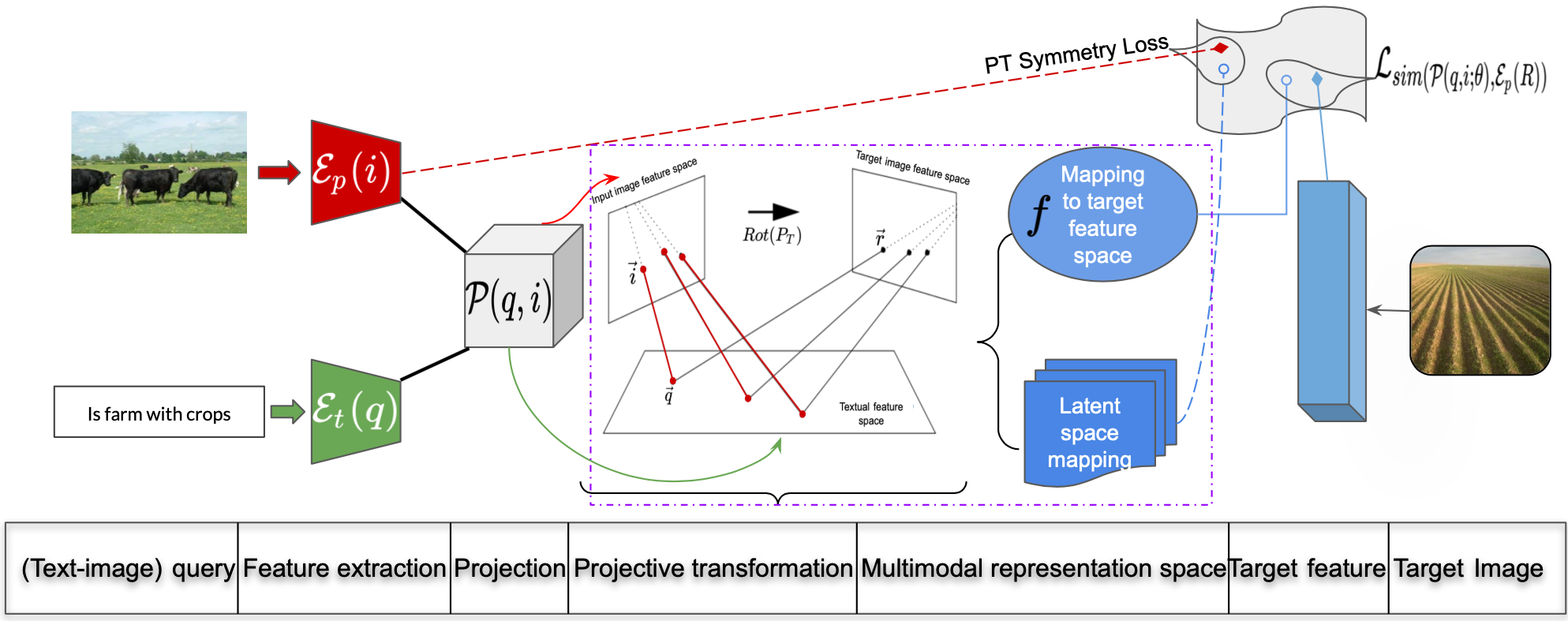
Semantic Hilbert Space for Interactive Image Retrieval
Amit Kumar Jaiswal, Haiming Liu, Ingo FrommholzProceedings of the 2021 ACM SIGIR International Conference on Theory of Information Retrieval (ICTIR) (ACM ICTIR), 2021
The paper introduces a model for interactive image retrieval utilising the geometrical framework of information retrieval (IR). We tackle the problem of image retrieval based on an expressive user information need in form of a textual-visual query, where a user is attempting to find an image similar to the picture in their mind during querying. The user information need is expressed using guided visual feedback based on Information Foraging which lets the user perception embed within the model via semantic Hilbert space (SHS). This framework is based on the mathematical formalism of quantum probabilities and aims to understand the relationship between user textual and image input, where the image in the input is considered a form of visual feedback. We propose SHS, a quantum-inspired approach where the textual-visual query is regarded analogously to a physical system that allows for modelling different... ...
[ Paper ] [ Poster ] [ Slides ] [BIBTEX ]
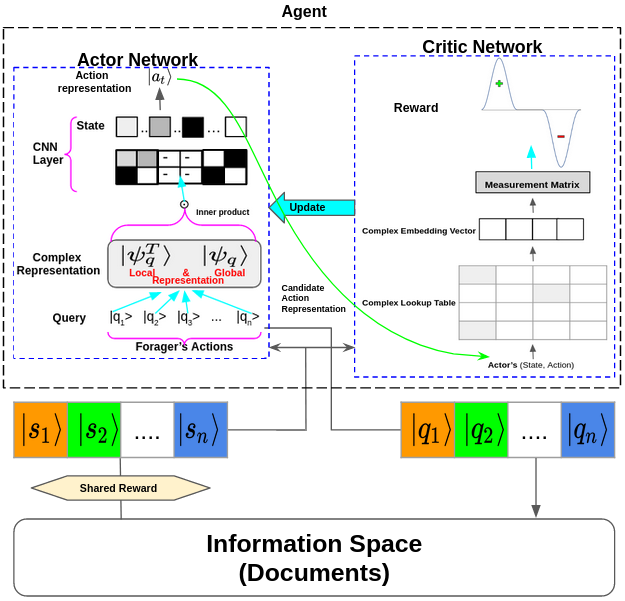
Reinforcement Learning-driven Information Seeking: A Quantum Probabilistic Approach
Amit Kumar Jaiswal, Haiming Liu, Ingo FrommholzProceedings of Bridging the Gap between Information Science, Information Retrieval and Data Science (BIRDS) (SIGIR), 2020
Understanding an information forager's actions during interaction is very important to the study of interactive information retrieval. Although information spread in uncertain information space is substantially complex due to the high entanglement of users’ interacting with information objects (text, image, etc.) and vice versa. However, an information forager, in general, accompanies a piece of information (information diet) while searching (or foraging) alternative contents, typically subject to decisive uncertainty. ...
[ Preprint ] [ Slides ] [BIBTEX ] [Video ]
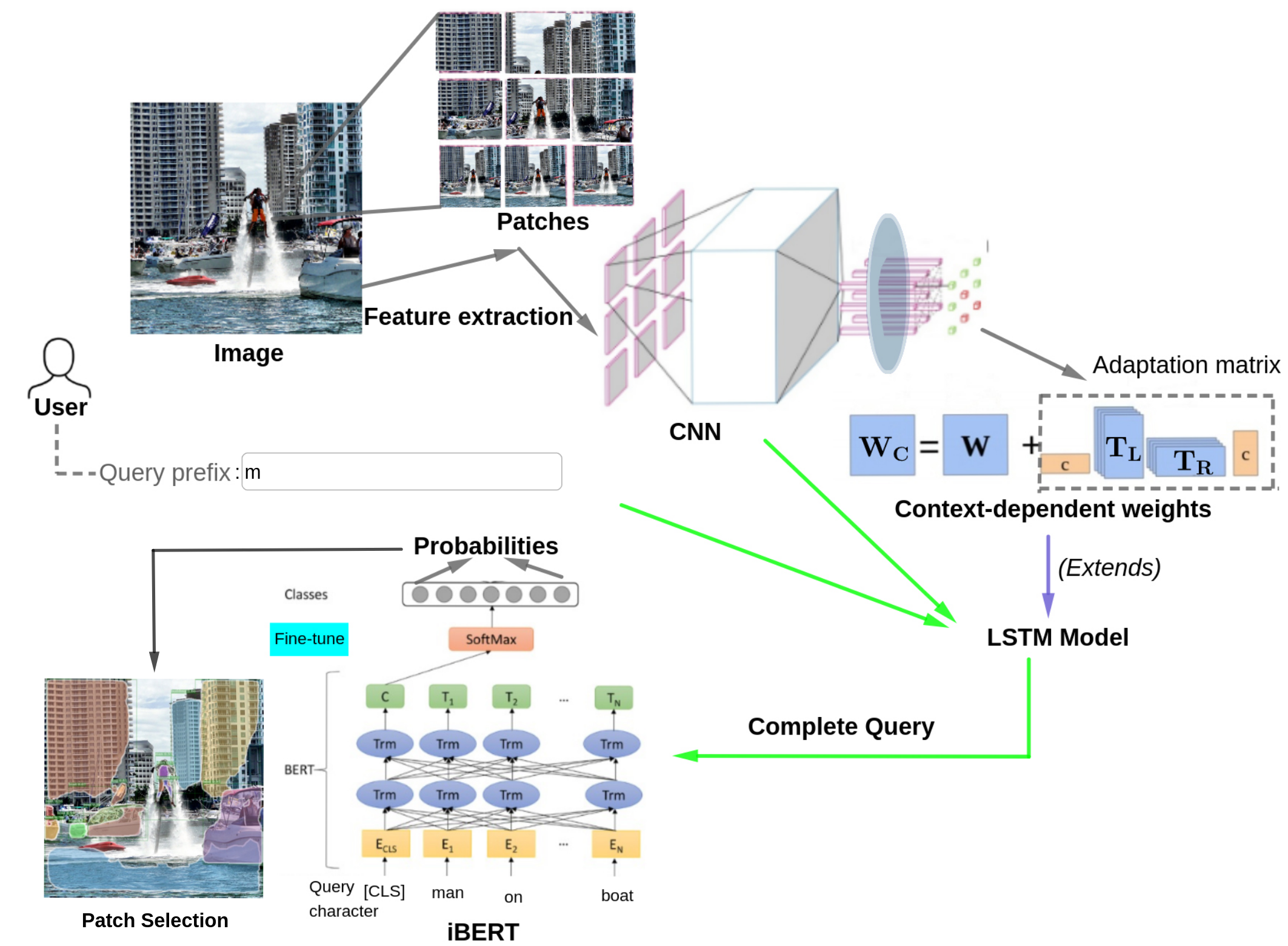
Utilising Information Foraging Theory for User Interaction with Image Query Auto-Completion
Amit Kumar Jaiswal, Haiming Liu, Ingo FrommholzProceedings of 42th European Conference on Information Retrieval (ECIR), 2020
Query Auto-completion (QAC) is a prominently used feature in search engines, where user interaction with such explicit feature is facilitated by the possible automatic suggestion of queries based on a prefix typed by the user. Existing QAC models have pursued a little on user interaction and cannot capture a user’s information need (IN) context. ...
[ Paper ] [Slides ] [BIBTEX ]
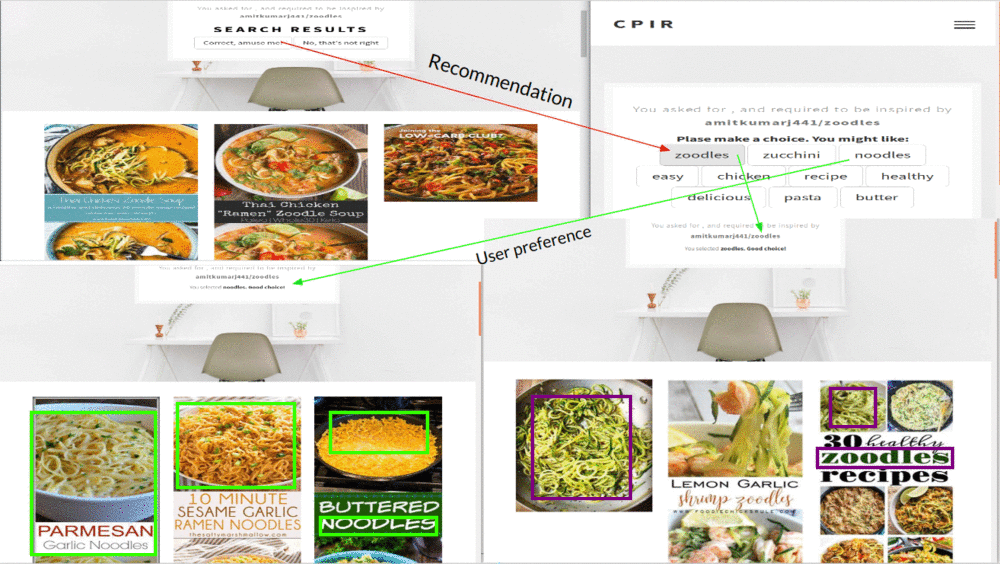
Information Foraging for Enhancing Implicit Feedback in Content-based Image Recommendation
Amit Kumar Jaiswal, Haiming Liu, Ingo FrommholzProceedings of the 11th annual meeting of the Forum for Information Retrieval Evaluation (FIRE), 2019
User implicit feedback plays an important role in recommender systems. However, finding implicit features is a tedious task. This paper aims to identify users' preferences through implicit behavioural signals for image recommendation based on the Information Scent Model of Information Foraging Theory. In the first part, we hypothesise that the users' perception is improved with visual cues in the images as behavioural signals that provide users' information scent during information seeking. ...
[ Paper ] [ Slides ] [ BIBTEX ]
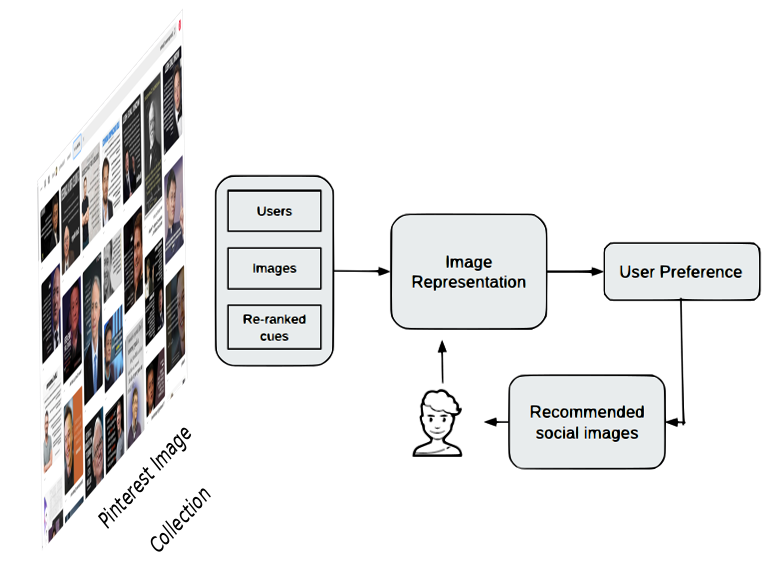
Effects of Foraging in Personalized Content-based Image Recommendation
Amit Kumar Jaiswal, Haiming Liu, Ingo FrommholzThe 2nd International Workshop on ExplainAble Recommendation and Search (EARS), SIGIR, 2019
A major challenge of recommender systems is to help users locating interesting items. Personalized recommender systems have become very popular as they attempt to predetermine the needs of users and provide them with recommendations to personalize their navigation. However, few studies have addressed the question of what drives the users’ attention to specific content within the collection and what influences the selection of interesting items. To this end, we employ the lens of Information Foraging Theory (IFT) to image recommendation to demonstrate how the user could utilize visual bookmarks to locate interesting images. ...
[ Paper ] [ Poster ] [ Slides ] [ BIBTEX ]
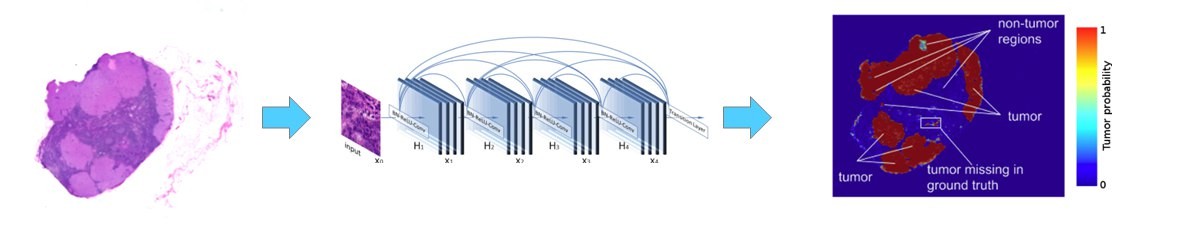
Semi-Supervised Learning for Cancer Detection of Lymph Node Metastases
Amit Kumar Jaiswal, Ivan Panshin, Dimitrij Shulkin, Nagender Aneja, Samuel AbramovWorkshop Towards Causal, Explainable and Universal Medical Visual Diagnosis, CVPR, 2019
Pathologists find tedious to examine the status of the sentinel lymph node on a large number of pathological scans. The examination process of such lymph node which encompasses metastasized cancer cells is histopathologically organized. However, the task of finding metastatic tissues is gradual which is often challenging. In this work, we present our deep convolutional neural network based model validated on PatchCamelyon (PCam) benchmark dataset for fundamental machine learning research in histopathology diagnosis. ...
[ Paper ] [ Poster ] [ BIBTEX ]
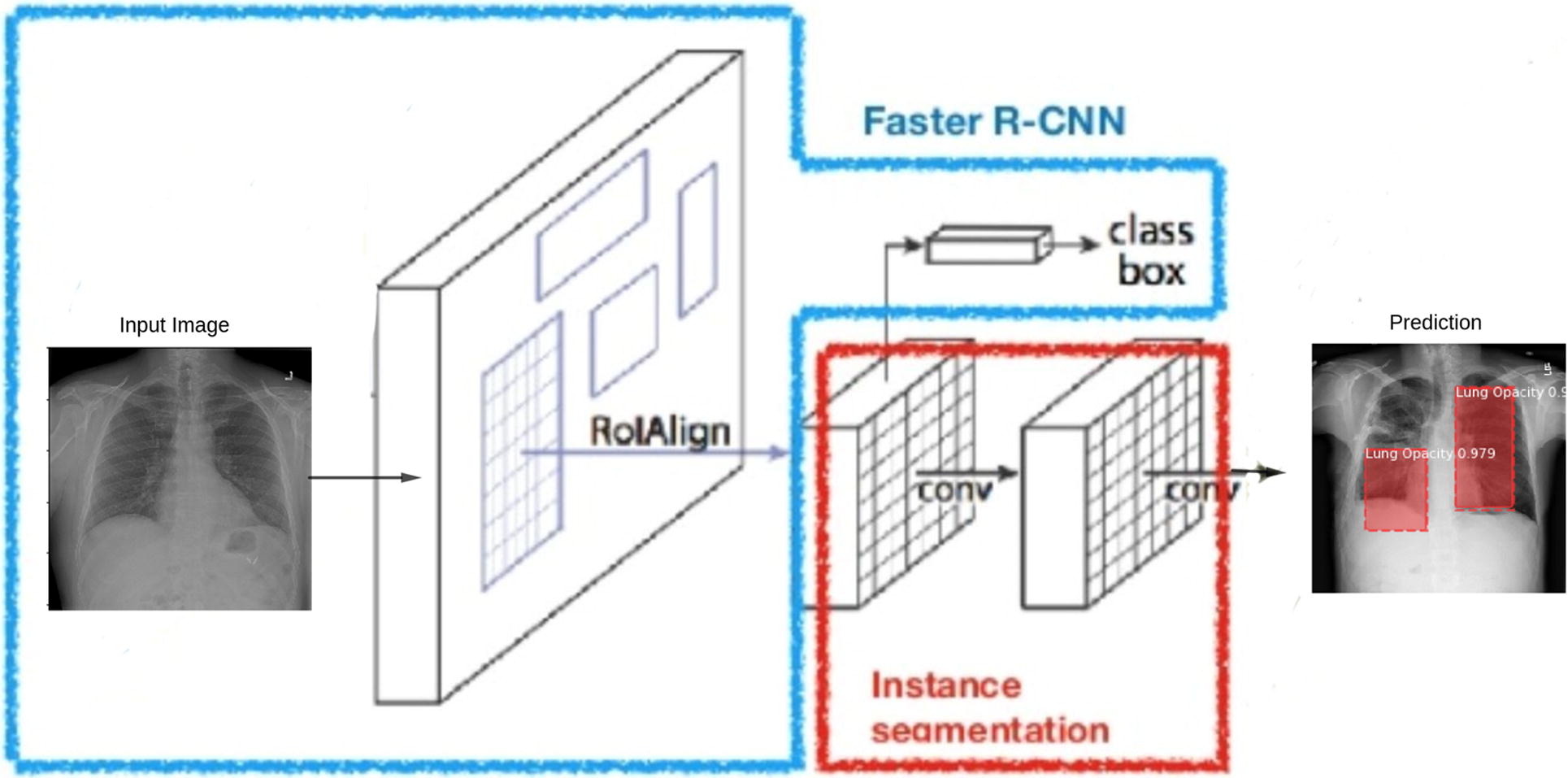
Identifying pneumonia in chest X-rays: A deep learning approach
Amit Kumar Jaiswal, P. Tiwari, S. Kumar, D. Gupta, A. Khanna & J. RodriguesJournal of Measurement, 2019
The rich collection of annotated datasets piloted the robustness of deep learning techniques to effectuate the implementation of diverse medical imaging tasks. Over 15% of deaths include children under age five are caused by pneumonia globally. In this study, we describe our deep learning based approach for the identification and localization of pneumonia in Chest X-rays (CXRs) images. Researchers usually employ CXRs for the diagnostic imaging study. Several factors such as positioning of the patient and depth of inspiration can change the appearance of the chest X-ray, complicating interpretation further. ...
[ Paper ] [ Code] [ BIBTEX ]
Quantum-like Generalization of Complex Word Embedding: A Lightweight Approach for Textual Classification
Amit Kumar Jaiswal, Guilherme Holdack, Ingo Frommholz, Haiming LiuFGIR, LWDA, 2018
In this paper, we present an extension, and an evaluation, to existing Quantum like approaches of word embedding for IR tasks that (1) improves complex features detection of word use (e.g., syntax and semantics), (2) enhances how this method extends these aforementioned uses across linguistic contexts (i.e., to model lexical ambiguity) - specifically Question Classification -, and (3) reduces computational resources needed for training and operating Quantum based neural networks, when confronted with existing models. ...
[ Paper ] [ BIBTEX ]
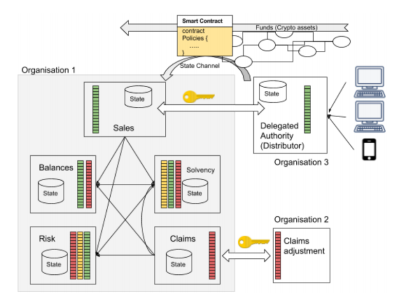
Parsec: A State Channel for the Internet of Value
Amit Kumar JaiswalOngoing Work, 2017
We propose Parsec, a web-scale State channel for the Internet of Value to exterminate the consensus bottleneck in Blockchain by leveraging a network of state channels which enable to robustly transfer value off-chain. It acts as an infrastructure layer developed on top of Ethereum Blockchain, as a network protocol which allows coherent routing and interlocking channel transfers for trade-off between parties. A web-scale solution for state channels is implemented to enable a layer of value transfer to the internet. Existing network protocol on State Channels include Raiden for Ethereum and Lightning Network for Bitcoin. ...
[ Preprint ] [ Code ] [ BIBTEX ]
Academic Activities
Web/Competition Chair @ CHILites, SIGCHI'19 HASOC,FIRE Conference'20,
Reviewer @ AISTATS 2026, ICLR 2026, JOSS '19-'24, IEEE TMI'20, ECIR'20, ACM ICMI'21, ECAI'23, ACMMM'23, MLGH, ICLR'23, SynS & ML, ICML'23, PLOS One, Re-Align Workshop, ICLR'25 , CogSci 2025, KDD 2025-2026, ICML 2025 Workshop on Assessing World Models.
Program Committee @ AAAI'25, WSDM'26, KDD'26, ACM RecSys'25, ACM CIKM'25, ACM SIGIR'25, ACM WebSci'25, ACM CIKM'24, ACM MM'24, ACM MM'23, ML4PS, NeurIPS '19-'22,'24
Talks
- [Oct 2022] Delivered a talk on Neural Ordinary Differential Equations (Neural ODEs) at University College London, United Kingdom.
- [Aug 2019] I gave a talk on Machine Learning for Protein Folding at Jean Golding Institute, University of Bristol, UK.
- [May 2019] I gave an invited talk at UNIPD Department of Information Engineering, University of Padova, Italy.
- [Dec 2017] I gave an invited talk on Cloud native computing for NFV at Open Source Networking Days, National Informatics Centre, Delhi.
- [Dec 2017] I gave an invited talk on Cloud Native Design/Refactoring across Kubernetes at the Kubernetes Contributor Summit at KubeCon+CloudNativeCon Austin, TX, US.
- [Nov 2017] I gave a talk on Big Iron in Little Clouds, or How I learned to make a better OpenStack cloud on z/VM at OpenStack Sydney Summit, Australia.
- [Nov 2017] I gave an invited talk on Hyperledger at BlockchainDevelopers Meetup.
- [June 2017] I gave an invited talk on Ethereum Blockchain at PyDelhi Meetup, India.
- [Mar 2017] I gave a talk on Web Development with Rust at Rust Hack Day, HBTU, Kanpur, India.
- [Jan 2017] I gave an invited talk on Diving into Docker: Developing a Darn Fast, Repeatable Workflow at WikiToLearn Conference, Jaipur, India.
 Github
Github LinkedIn
LinkedIn Google Scholar
Google Scholar DBLP
DBLP